Appearance
Tutorial 4 - Data Gathering
This tutorial focuses on establishing a reliable foundation for your energy modelling through effective data gathering and validation. Quality data is the cornerstone of accurate energy system analysis, enabling confident decision-making and reliable performance predictions.
Intent
Firm Basis of Truth
Establishing a reliable data foundation for accurate modelling begins with eliminating assumptions wherever possible through measured data. Creating transparency in data sources and quality builds stakeholder confidence through evidence-based analysis. The goal is to move from theoretical estimates to measured reality, providing a solid foundation for all further modelling work.
Understanding the Problem
Defining energy system requirements and constraints starts with identifying key performance indicators and success metrics. Understanding site-specific conditions and limitations, along with characterising demand patterns and energy usage profiles, ensures your model reflects the actual operating environment rather than theoretical conditions.
Purpose in Encast
Data Quality
The importance of measurement data overestimated profiles cannot be overstated. Understanding data resolution requirements-whether half-hourly, daily, or monthly-affects model accuracy and computational efficiency. Validation and error checking of imported datasets help maintain data integrity, while managing data gaps and interpolation methods ensures continuous analysis capability. Regular comparison between actual vs modelled performance validates your assumptions and identifies areas for improvement.
Timestep
Selecting appropriate modelling timesteps for different systems requires understanding when high-resolution data is critical. Balancing computational efficiency with accuracy requirements means considering seasonal and diurnal variation patterns that affect system performance. Some systems require minute-by-minute resolution, while others perform adequately with daily aggregation.
Digital Twin
Creating representative models of existing systems involves calibrating models against real performance data. Ongoing model validation and refinement ensure your digital twin remains accurate over time. Using digital twins for scenario planning and optimisation allows you to test proposed changes without disrupting actual operations.
Real Time Prediction
Real-time prediction capabilities enable dynamic system management and immediate response to changing conditions. This functionality bridges the gap between historical analysis and planning, providing immediate insights for operational decision-making.
Process
Start
Begin by identifying all available data sources on site, from existing metering systems to manual records. Establishing measurement protocols for missing data ensures comprehensive coverage of your energy system. Creating data collection templates and procedures standardises the gathering process, while setting up monitoring systems where needed fills critical gaps in your data landscape.
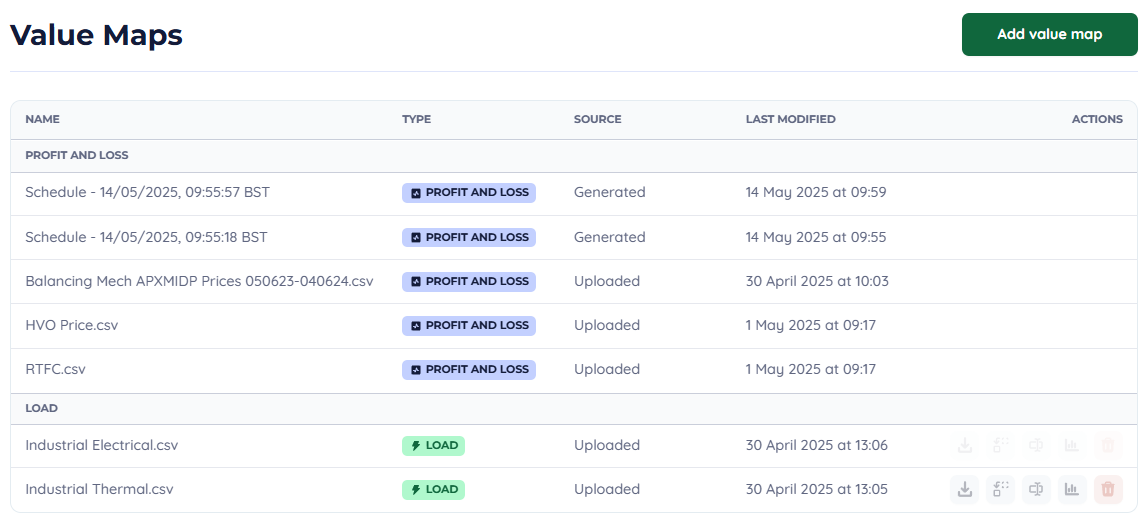
When uploading data to Encast, ensure your CSV files match the expected format. The system accepts various data types, including electrical demand, generation output, and environmental conditions. Use the value map upload feature to import your historical data.
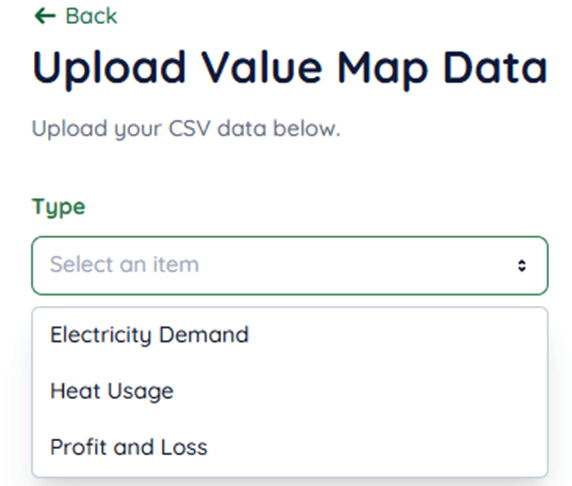
Middle
Ongoing data validation and quality control maintain model accuracy throughout the project lifecycle. Regular comparison between modelled and actual performance helps identify model drift and calibration needs. Identifying and investigating performance anomalies reveals system issues or model assumptions that require attention. Documenting lessons learned and model improvements create an institutional knowledge base for future projects.
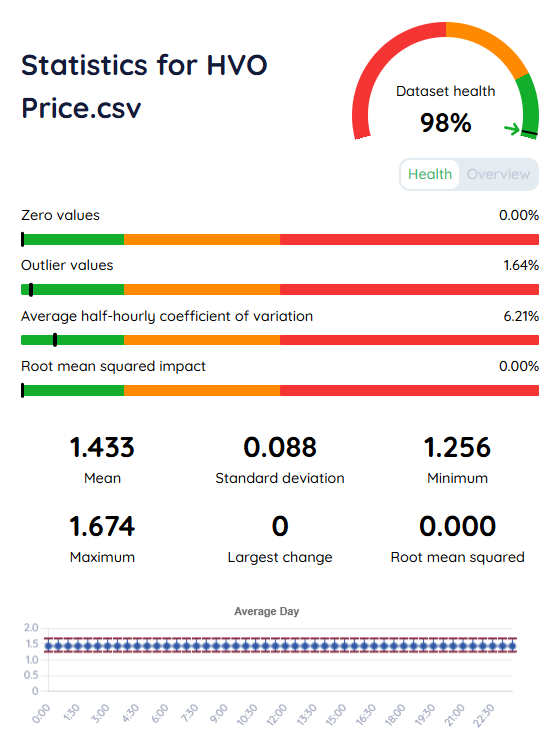
Use the headroom analysis tool to compare predicted vs actual performance. Significant deviations indicate either data quality issues or model assumptions that need refinement.
End
Final model validation against complete datasets provides confidence in your analysis results. Documentation of data sources and assumptions ensures reproducibility and enables future model updates. Creating recommendations for ongoing monitoring establishes protocols for maintaining model accuracy over time.
Continuous Development and Model Iteration
Rapid Iteration
Using sensitivity studies to test different scenarios quickly enables agile decision-making. Implementing feedback loops between model and reality ensures your analysis remains grounded in actual performance. An agile approach to model refinement and improvement allows rapid incorporation of new insights. Quick validation of proposed system changes reduces project risk and implementation time.
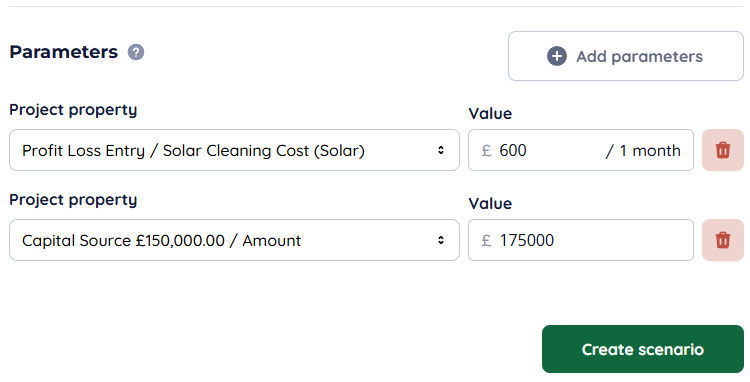
The scenario comparison feature allows rapid testing of different assumptions and configurations, helping identify the most robust solutions.
New Information
Incorporating updated equipment specifications keeps your model current with actual installations. Adapting to changing operational requirements ensures the continued relevance of your analysis. Including new regulatory or economic conditions maintains the business case accuracy. Learning from operational experience and maintenance data improves future model accuracy.
Evolving Model
Version control and change tracking document model evolution and decision rationale. Maintaining model accuracy as systems change over time requires systematic updating procedures. Planning for future system expansions and modifications ensures your model can grow with your energy system.
Use the scenario versioning feature to track changes and maintain historical analysis capability.
Working with Measured Data
When importing measured data into Encast, pay attention to the data resolution and quality. Half-hourly data provides good resolution for most applications, while daily data may be enough for long-term planning.
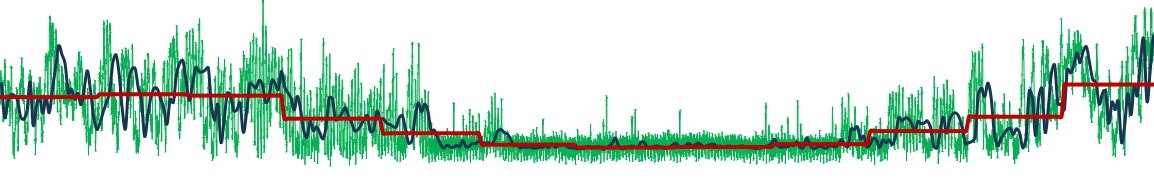
Check for data gaps and inconsistencies before importing. Use the data validation tools to identify outliers and potential measurement errors.
Calibration Process
Calibrating your model against measured performance involves comparing predicted outputs with actual results across multiple operating conditions. Use the detail view to examine specific periods where discrepancies occur.
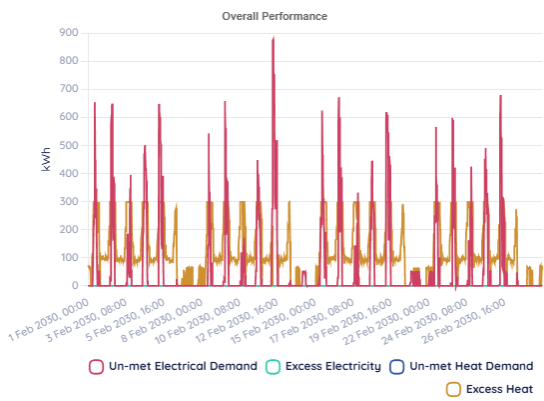
Focus on periods with different operating conditions-high and low demand, various weather conditions, and different equipment configurations-to ensure your model performs well across all scenarios.
Data Quality Metrics
Establish data quality metrics to track the reliability of your inputs. These might include:
- Percentage of missing data points
- Frequency of outlier values
- Comparison accuracy between predicted and actual performance
- Data collection consistency over time
Conclusion
Effective data gathering transforms energy modelling from a theoretical exercise to a practical engineering tool. By establishing reliable data sources, implementing quality control processes, and maintaining continuous model validation, you create a foundation for confident decision-making. The investment in quality data gathering pays dividends throughout the project lifecycle, enabling accurate performance prediction, reliable financial analysis, and successful system optimisation.
Remember that data gathering is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process that improves your model accuracy and decision-making capability over time. Start with the best available data, implement systematic validation processes, and continuously refine your approach based on operational experience.